Seattle - Bullitt Center 01 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the
 The second and most dramatic boom resulted from the Klondike Gold Rush, which ended the depression that had begun with the Panic of 1893. In a short time, Seattle became a major transportation center. On July 14, 1897, the ''S.S. Portland'' docked with its famed "ton of gold," and Seattle became the main transport and supply point for the miners in Alaska and the Yukon. Few of those working men found lasting wealth. However, it was Seattle's business of clothing the miners and feeding them salmon that panned out in the long run. Along with Seattle, other cities like Everett, Tacoma, Port Townsend,
The second and most dramatic boom resulted from the Klondike Gold Rush, which ended the depression that had begun with the Panic of 1893. In a short time, Seattle became a major transportation center. On July 14, 1897, the ''S.S. Portland'' docked with its famed "ton of gold," and Seattle became the main transport and supply point for the miners in Alaska and the Yukon. Few of those working men found lasting wealth. However, it was Seattle's business of clothing the miners and feeding them salmon that panned out in the long run. Along with Seattle, other cities like Everett, Tacoma, Port Townsend,  The famous ''
The famous ''
 War work again brought local prosperity during World War II, this time centered on Boeing aircraft. The war dispersed the city's numerous Japanese-American businessmen due to the
War work again brought local prosperity during World War II, this time centered on Boeing aircraft. The war dispersed the city's numerous Japanese-American businessmen due to the
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The Seattle metropolitan area
The Seattle metropolitan area is an urban conglomeration in the U.S. state of Washington that comprises Seattle, its surrounding satellites and suburbs. It contains the three most populous counties in the state—King, Snohomish, and Pierce ...
's population is 4.02 million, making it the 15th-largest in the United States. Its growth rate of 21.1% between 2010 and 2020 makes it one of the nation's fastest-growing large cities.
Seattle is situated on an isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
between Puget Sound (an inlet of the Pacific Ocean) and Lake Washington. It is the northernmost major city in the United States, located about south of the Canadian border
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
. A major gateway for trade with East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
, Seattle is the fourth-largest port in North America in terms of container handling .
The Seattle area was inhabited by Native Americans for at least 4,000 years before the first permanent European settlers. Arthur A. Denny and his group of travelers, subsequently known as the Denny Party
The Denny Party is a group of American pioneers credited with founding Seattle, Washington. They settled at Alki Point on November 13, 1851.
History
A wagon party headed by Arthur A. Denny left Cherry Grove, Illinois on April 10, 1851. The part ...
, arrived from Illinois via Portland, Oregon
Portland (, ) is a port city in the Pacific Northwest and the list of cities in Oregon, largest city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Situated at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, Columbia rivers, Portland is ...
, on the schooner ''Exact'' at Alki Point on November 13, 1851. The settlement was moved to the eastern shore of Elliott Bay and named "Seattle" in 1852, in honor of Chief Si'ahl of the local Duwamish and Suquamish
The Suquamish () are a Lushootseed language, Lushootseed-speaking Native Americans in the United States, Native American people, located in present-day Washington (state), Washington in the United States. They are a southern Coast Salish peopl ...
tribes. Today, Seattle has high populations of Native, Scandinavian, European American, Asian American and African American people, as well as a thriving LGBT community that ranks sixth in the United States by population.
Logging was Seattle's first major industry, but by the late 19th century, the city had become a commercial and shipbuilding center as a gateway to Alaska during the Klondike Gold Rush. Growth after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
was partially due to the local Boeing company, which established Seattle as a center for aircraft manufacturing. The Seattle area developed into a technology center from the 1980s onwards with companies like Microsoft becoming established in the region; Microsoft founder Bill Gates is a Seattleite by birth. Internet retailer Amazon was founded in Seattle in 1994, and major airline Alaska Airlines
Alaska Airlines is a major American airline headquartered in SeaTac, Washington, within the Seattle metropolitan area. It is the sixth largest airline in North America when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and the num ...
is based in SeaTac, Washington, serving Seattle's international airport, Seattle–Tacoma International Airport
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport , branded as SEA Airport and also referred to as Sea–Tac (), is the primary commercial airport serving the Seattle metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Washington. It is in the city of SeaTac, which ...
. The stream of new software, biotechnology, and Internet companies led to an economic revival, which increased the city's population by almost 50,000 between 1990 and 2000. Seattle also has a significant musical history. Between 1918 and 1951, nearly two dozen jazz nightclubs existed along Jackson Street, from the current Chinatown/International District to the Central District. The jazz scene nurtured the early careers of Ray Charles, Quincy Jones
Quincy Delight Jones Jr. (born March 14, 1933) is an American record producer, musician, songwriter, composer, arranger, and film and television producer. His career spans 70 years in the entertainment industry with a record of 80 Grammy Award n ...
, Ernestine Anderson
Ernestine Anderson (November 11, 1928 – March 10, 2016) was an American jazz and blues singer. In a career spanning more than six decades, she recorded over 30 albums. She was nominated four times for a Grammy Award. She sang at Carnegie Hall, ...
, and others. Seattle is also the birthplace of rock musician Jimi Hendrix, as well as the origin of the bands Nirvana, Pearl Jam, Soundgarden, Heart, Alice in Chains
Alice in Chains (often abbreviated as AIC) is an American rock band from Seattle, Washington, formed in 1987 by guitarist and vocalist Jerry Cantrell and drummer Sean Kinney, who later recruited bassist Mike Starr and lead vocalist Layne ...
, Foo Fighters, and the alternative rock movement grunge.
History
Founding
Archaeological excavations suggest that Native Americans have inhabited the Seattle area for at least 4,000 years. By the time the first European settlers arrived, the people (subsequently called theDuwamish tribe
The Duwamish ( lut, Dxʷdəwʔabš, ) are a Lushootseed-speaking Native American tribe in western Washington, and the indigenous people of metropolitan Seattle, where they have been living since the end of the last glacial period (c. 8000 BCE ...
) occupied at least seventeen villages in the areas around Elliott Bay.
The first European to visit the Seattle area was George Vancouver, in May 1792 during his 1791–95 expedition for the Royal Navy to chart the Pacific Northwest.
In 1851, a large party of American pioneers led by Luther Collins made a location on land at the mouth of the Duwamish River; they formally claimed it on September 14, 1851. Thirteen days later, members of the Collins Party on the way to their claim passed three scouts of the Denny Party. Members of the Denny Party claimed land on Alki Point on September 28, 1851. The rest of the Denny Party set sail on the schooner ''Exact'' from Portland, Oregon, stopping in Astoria, and landed at Alki Point during a rainstorm on November 13, 1851. After a difficult winter, most of the Denny Party relocated across Elliott Bay and claimed land a second time at the site of present-day Pioneer Square, naming this new settlement ''Duwamps''.
Charles Terry and John Low remained at the original landing location, reestablished their old land claim and called it "New York", but renamed "New York Alki" in April 1853, from a Chinook word meaning, roughly, "by and by" or "someday". For the next few years, New York Alki and Duwamps competed for dominance, but in time Alki was abandoned and its residents moved across the bay to join the rest of the settlers. David Swinson "Doc" Maynard, one of the founders of Duwamps, was the primary advocate to name the settlement Seattle after Chief Si'ahl ( lut, siʔaɫ, anglicized as "Seattle") chief of the Duwamish and Suquamish
The Suquamish () are a Lushootseed language, Lushootseed-speaking Native Americans in the United States, Native American people, located in present-day Washington (state), Washington in the United States. They are a southern Coast Salish peopl ...
tribes. Includes bibliography. A modern transliteration of the original Coast Salish settlements around Elliott Bay is rendered in Lushootseed
Lushootseed (txʷəlšucid, dxʷləšúcid), also Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish or Skagit-Nisqually, is a language made up of a dialect continuum of several Salish tribes of modern-day Washington state. Lushootseed is one of the Coast Salis ...
as .
The name "Seattle" appears on official Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the ...
papers dated May 23, 1853, when the first plats for the village were filed. In 1855, nominal land settlements were established. On January 14, 1865, the Legislature of Territorial Washington incorporated the Town of Seattle with a board of trustees managing the city. The Town of Seattle was disincorporated on January 18, 1867, and remained a mere precinct of King County until late 1869, when a new petition was filed and the city was re-incorporated December 2, 1869, with a mayor–council government. The corporate seal of the City of Seattle carries the date "1869" and a likeness of Chief Si'ahl in left profile. That same year, Seattle acquired the epithet of the "Queen City", a designation officially changed in 1982 to "Emerald City".
Timber town
Seattle has a history of boom-and-bust cycles, like many other cities near areas of extensive natural and mineral resources. Seattle has risen several times economically, then gone into precipitous decline, but it has typically used those periods to rebuild solid infrastructure. Author has granted blanket permission for material from that paper to be reused in Wikipedia. Now at s:Seattle: Booms and Busts. The first such boom, covering the early years of the city, rode on the lumber industry. During this period the road now known asYesler Way
Yesler Way is an east–west street in Seattle named for Henry Yesler, the founder of Seattle. East–west streets in Seattle south of Yesler Way are prefixed "South"; avenues are suffixed with "South" as they cross Yesler Way. The street origina ...
won the nickname "Skid Road," supposedly after the timber skidding down the hill to Henry Yesler
Henry Leiter Yesler (December 2, 1810 – December 16, 1892) was an entrepreneur and a politician, regarded as a founder of the city of Seattle. Yesler served two non-consecutive terms as Mayor of Seattle, and was the city's wealthiest resident ...
's sawmill. The later dereliction of the area may be a possible origin for the term which later entered the wider American lexicon as ''Skid Row
A skid row or skid road is an impoverished area, typically urban, in English-speaking North America whose inhabitants are mostly poor people " on the skids". This specifically refers to poor or homeless, considered disreputable, downtrodden or fo ...
''.
Like much of the American West, Seattle saw numerous conflicts between labor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the la ...
and management, as well as ethnic tensions that culminated in the anti-Chinese riots of 1885–1886. This violence originated with unemployed whites who were determined to drive the Chinese from Seattle (anti-Chinese riots also occurred in Tacoma). In 1900, Asians were 4.2% of the population.
Authorities declared martial law and federal troops arrived to put down the disorder.
Seattle had achieved sufficient economic success that when the Great Seattle Fire
The Great Seattle Fire was a fire that destroyed the entire central business district of Seattle, Washington on June 6, 1889. The conflagration lasted for less than a day, burning through the afternoon and into the night, and during the same sum ...
of 1889 destroyed the central business district, a far grander city-center rapidly emerged in its place.
Finance company Washington Mutual
Washington Mutual (often abbreviated to WaMu) was the United States' largest savings and loan association until its collapse in 2008.
A savings bank holding company is defined in United States Code: Title 12: Banks and Banking; Section 1842: Def ...
, for example, was founded in the immediate wake of the fire.
However, the Panic of 1893 hit Seattle hard.
Gold Rush, World War I, and the Great Depression
 The second and most dramatic boom resulted from the Klondike Gold Rush, which ended the depression that had begun with the Panic of 1893. In a short time, Seattle became a major transportation center. On July 14, 1897, the ''S.S. Portland'' docked with its famed "ton of gold," and Seattle became the main transport and supply point for the miners in Alaska and the Yukon. Few of those working men found lasting wealth. However, it was Seattle's business of clothing the miners and feeding them salmon that panned out in the long run. Along with Seattle, other cities like Everett, Tacoma, Port Townsend,
The second and most dramatic boom resulted from the Klondike Gold Rush, which ended the depression that had begun with the Panic of 1893. In a short time, Seattle became a major transportation center. On July 14, 1897, the ''S.S. Portland'' docked with its famed "ton of gold," and Seattle became the main transport and supply point for the miners in Alaska and the Yukon. Few of those working men found lasting wealth. However, it was Seattle's business of clothing the miners and feeding them salmon that panned out in the long run. Along with Seattle, other cities like Everett, Tacoma, Port Townsend, Bremerton
Bremerton is a city in Kitsap County, Washington. The population was 37,729 at the 2010 census and an estimated 41,405 in 2019, making it the largest city on the Kitsap Peninsula. Bremerton is home to Puget Sound Naval Shipyard and the Bremer ...
, and Olympia, all in the Puget Sound region, became competitors for exchange, rather than mother lodes for extraction, of precious metals. The boom lasted well into the early part of the 20th century, and funded many new Seattle companies and products. In 1907, 19-year-old James E. Casey borrowed $100 from a friend and founded the American Messenger Company (later UPS). Other Seattle companies founded during this period include Nordstrom and Eddie Bauer
Eddie Bauer, LLC is an American clothing store chain headquartered in Seattle, Seattle, Washington. Eddie Bauer sells its merchandise via retail stores, outlet stores, and online and via phone, with a call center in Groveport, Ohio. Its flagship ...
. Seattle brought in the Olmsted Brothers
The Olmsted Brothers company was a landscape architectural firm in the United States, established in 1898 by brothers John Charles Olmsted (1852–1920) and Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. (1870–1957), sons of the landscape architect Frederick Law O ...
landscape architecture firm to design a system of parks and boulevards.
The Gold Rush era culminated in the Alaska-Yukon-Pacific Exposition of 1909, which is largely responsible for the layout of today's University of Washington campus.
A shipbuilding boom in the early part of the 20th century became massive during World War I, making Seattle somewhat of a company town. The subsequent retrenchment led to the Seattle General Strike of 1919
The Seattle General Strike of 1919 was a five-day general work stoppage by more than 65,000 workers in the city of Seattle, Washington from February 6 to 11. Dissatisfied workers in several unions began the strike to gain higher wages, after two ...
, the first general strike in the country. A 1912 city development plan by Virgil Bogue went largely unused. Seattle was mildly prosperous in the 1920s but was particularly hard hit in the Great Depression, experiencing some of the country's harshest labor strife in that era. Violence during the Maritime Strike of 1934 cost Seattle much of its maritime traffic, which was rerouted to the Port of Los Angeles.
The Great Depression in Seattle affected many minority groups, one being the Asian Pacific Americans; they were subject to racism, loss of property, and failed claims of unemployment due to citizenship status.
Seattle was one of the major cities that benefited from programs such as the WPA
WPA may refer to:
Computing
*Wi-Fi Protected Access, a wireless encryption standard
*Windows Product Activation, in Microsoft software licensing
* Wireless Public Alerting (Alert Ready), emergency alerts over LTE in Canada
* Windows Performance An ...
, CCC, UCL, and PWA. The workers, mostly men, built roads, parks, dams, schools, railroads, bridges, docks, and even historical and archival record sites and buildings. However, Seattle faced massive unemployment, loss of lumber and construction industries as Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
prevailed as the bigger West Coast city. Seattle had building contracts that rivaled New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
, but lost to LA as well. Seattle's eastern farm land faded due to Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
's and the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
's, forcing people into town.
 The famous ''
The famous ''Hooverville A "Hooverville" was a shanty town built during the Great Depression by the homeless in the United States. They were named after Herbert Hoover, who was President of the United States during the onset of the Depression and was widely blamed for it. ...
'' arose during the Depression, leading to Seattle's growing homeless population. Stationed outside Seattle, the Hooverville housed thousands of men but very very few children and no women. With work projects close to the city, Hooverville grew and the WPA settled into the city.
A movement by women arose from Seattle during the Depression. Fueled by Eleanor Roosevelt
Anna Eleanor Roosevelt () (October 11, 1884November 7, 1962) was an American political figure, diplomat, and activist. She was the first lady of the United States from 1933 to 1945, during her husband President Franklin D. Roosevelt's four ...
's book ''It's Up to the Women'', women pushed for recognition, not just as housewives, but as the backbone to family. Using newspapers and journals ''Working Woman'' and ''The Woman Today'', women pushed to be seen as equal and receive some recognition.
Seattle's University of Washington was greatly affected during the Depression era. As schools across Washington lost funding and attendance, the UW actually prospered during the time period. While Seattle public schools
Seattle Public Schools is the largest Public school (government funded), public school district in the state of Washington (state), Washington. The school district serves almost all of Seattle. Additionally it includes sections of Boulevard Park, ...
were influenced by Washington's superintendent Worth McClure, they still struggled to pay teachers and maintain attendance. The UW, despite academic challenges that plagued the college due to differing views on teaching and learning, focused on growth in student enrollment rather than improving the existing school.
Seattle was also the home base of impresario Alexander Pantages who, starting in 1902, opened a number of theaters in the city exhibiting vaudeville
Vaudeville (; ) is a theatrical genre of variety entertainment born in France at the end of the 19th century. A vaudeville was originally a comedy without psychological or moral intentions, based on a comical situation: a dramatic composition ...
acts and silent movies. He went on to became one of America's greatest theater and movie tycoons. Scottish-born architect B. Marcus Priteca designed several theaters for Pantages in Seattle, which were later demolished or converted to other uses. Seattle's surviving Paramount Theatre, on which he collaborated, was not a Pantages theater.
Post-war years: aircraft and software
 War work again brought local prosperity during World War II, this time centered on Boeing aircraft. The war dispersed the city's numerous Japanese-American businessmen due to the
War work again brought local prosperity during World War II, this time centered on Boeing aircraft. The war dispersed the city's numerous Japanese-American businessmen due to the Japanese American internment
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. After the war, the local economy dipped. It rose again with Boeing's growing dominance in the commercial airliner
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an ...
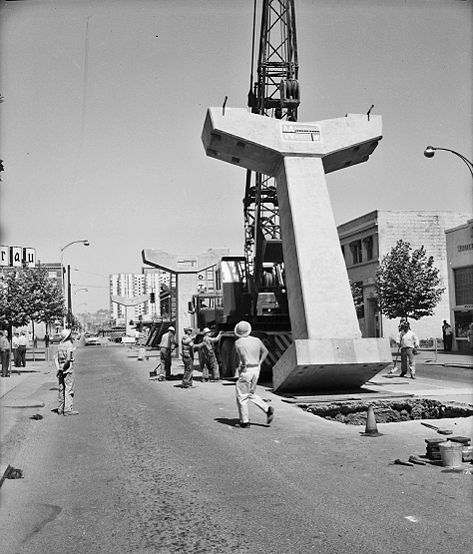
market. Seattle celebrated its restored prosperity and made a bid for world recognition with the Century 21 Exposition
The Century 21 Exposition (also known as the Seattle World's Fair) was a world's fair held April 21, 1962, to October 21, 1962, in Seattle, Washington, United States.1962 World's Fair, for which the iconic
 Seattle is located between the saltwater Puget Sound (an arm of the Pacific Ocean) to the west and Lake Washington to the east. The city's chief harbor, Elliott Bay, is part of Puget Sound, which makes the city an oceanic port. To the west, beyond Puget Sound, are the
Seattle is located between the saltwater Puget Sound (an arm of the Pacific Ocean) to the west and Lake Washington to the east. The city's chief harbor, Elliott Bay, is part of Puget Sound, which makes the city an oceanic port. To the west, beyond Puget Sound, are the
Space Needle
The Space Needle is an observation tower in Seattle, Washington, United States. Considered to be an icon of the city, it has been designated a Seattle landmark. Located in the Lower Queen Anne neighborhood, it was built in the Seattle Center f ...
was built. Another major local economic downturn was in the late 1960s and early 1970s, at a time when Boeing was heavily affected by the oil crises, loss of government contracts, and costs and delays associated with the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
. Many people left the area to look for work elsewhere, and two local real estate agents put up a billboard reading "Will the last person leaving Seattle – Turn out the lights."
Seattle remained the corporate headquarters of Boeing until 2001, when the company separated its headquarters from its major production facilities; the headquarters were moved to Chicago. The Seattle area is still home to Boeing's Renton narrow-body plant and Everett wide-body plant. The company's credit union
A credit union, a type of financial institution similar to a commercial bank, is a member-owned nonprofit organization, nonprofit financial cooperative. Credit unions generally provide services to members similar to retail banks, including depo ...
for employees, BECU
BECU is a credit union originally established to serve employees of Boeing, The Boeing Company. BECU was founded as Fellowship Credit Union in 1935 by 18 Boeing employees, and was named Boeing Employees' Credit Union for much of its history. It ...
, remains based in the Seattle area and has been open to all residents of Washington since 2002.
On March 20, 1970, twenty-eight people were killed when the Ozark Hotel was burned by an unknown arsonist.
As prosperity began to return in the 1980s, the city was stunned by the Wah Mee massacre
The Wah Mee massacre () was a mass shooting that occurred during the night of February 18–19, 1983, in which Kwan Fai "Willie" Mak, Wai Chiu "Tony" Ng, and Keung Kin "Benjamin" Ng (no relation) bound, robbed, and shot fourteen people in the Wa ...
in 1983, when thirteen people were killed in an illegal gambling club in the Seattle Chinatown-International District
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region of N ...
. Beginning with Microsoft's 1979 move from Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
, New Mexico, to nearby Bellevue, Washington
Bellevue ( ) is a city in the Eastside region of King County, Washington, United States, located across Lake Washington from Seattle. It is the third-largest city in the Seattle metropolitan area and has variously been characterized as a s ...
, Seattle and its suburbs became home to a number of technology companies including Amazon, F5 Networks
F5, Inc. is an American technology company specializing in application security, multi-cloud management, online fraud prevention, application delivery networking (ADN), application availability & performance, network security, and access & autho ...
, RealNetworks
RealNetworks, Inc. is a provider of artificial intelligence and computer vision based products. RealNetworks was a pioneer in Internet streaming software and services. They are based in Seattle, Washington, United States. The company also p ...
, Nintendo of America
is a Japanese multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produced handmade playing cards. ...
, and T-Mobile
T-Mobile is the brand name used by some of the mobile communications subsidiaries of the German telecommunications company Deutsche Telekom AG in the Czech Republic (T-Mobile Czech Republic), Poland (T-Mobile Polska), the United States (T-Mobile ...
. This success brought an influx of new residents with a population increase within city limits of almost 50,000 between 1990 and 2000, and saw Seattle's real estate become some of the most expensive in the country. In 1993, the movie ''Sleepless in Seattle
''Sleepless in Seattle'' is a 1993 American romantic comedy-drama film directed by Nora Ephron, from a screenplay she wrote with David S. Ward and Jeff Arch. Starring Tom Hanks and Meg Ryan, the film follows a journalist (Ryan) who, despite be ...
'' brought the city further national attention, as did the television sitcom ''Frasier
''Frasier'' () is an American television sitcom that was broadcast on NBC for 11 seasons. It premiered on September 16, 1993, and ended on May 13, 2004. The program was created and produced by David Angell, Peter Casey (screenwriter), Peter Case ...
''. The dot-com boom
The dot-com bubble (dot-com boom, tech bubble, or the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Compos ...
caused a great frenzy among the technology companies in Seattle but the bubble ended in early 2001.
Seattle in this period attracted widespread attention as home to these many companies, but also by hosting the 1990 Goodwill Games
The Goodwill Games were an international sports competition created by Ted Turner in reaction to the political troubles surrounding the Olympic Games of the 1980s. In 1979, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan caused the United States and other ...
and the APEC
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC ) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
leaders conference in 1993, as well as through the worldwide popularity of grunge, a sound that had developed in Seattle's independent music scene. Another bid for worldwide attention—hosting the World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference of 1999
The WTO Ministerial Conference of 1999 was a meeting of the World Trade Organization, convened at the Washington State Convention and Trade Center in Seattle, Washington, USA, over the course of three days, beginning Tuesday, 30 November 1999. ...
—garnered visibility, but not in the way its sponsors desired, as related protest activity and police reactions to those protests overshadowed the conference itself. The city was further shaken by the Mardi Gras Riots in 2001, and then literally shaken the following day by the Nisqually earthquake
The 2001 Nisqually earthquake occurred at on February 28, 2001 and lasted nearly a minute. The intraslab earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). The epicenter was in the southern Puget So ...
.
Another boom began as the city emerged from the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
which commenced when Amazon.com moved its headquarters from North Beacon Hill to South Lake Union
South Lake Union (sometimes SLU) is a neighborhood in Seattle, Washington, so named because it is at the southern tip of Lake Union.
The official boundaries of the City of Seattle Urban Center are Denny Way on the south, beyond which is Den ...
. This initiated a historic construction boom which resulted in the completion of almost 10,000 apartments in Seattle in 2017, which is more than any previous year and nearly twice as many as were built in 2016. Beginning in 2010, and for the next five years, Seattle gained an average of 14,511 residents per year, with the growth strongly skewed toward the center of the city, as unemployment dropped from roughly 9 percent to 3.6 percent. The city has found itself "bursting at the seams", with over 45,000 households spending more than half their income on housing and at least 2,800 people homeless, and with the country's sixth-worst rush hour traffic.
Geography
Topography
 Seattle is located between the saltwater Puget Sound (an arm of the Pacific Ocean) to the west and Lake Washington to the east. The city's chief harbor, Elliott Bay, is part of Puget Sound, which makes the city an oceanic port. To the west, beyond Puget Sound, are the
Seattle is located between the saltwater Puget Sound (an arm of the Pacific Ocean) to the west and Lake Washington to the east. The city's chief harbor, Elliott Bay, is part of Puget Sound, which makes the city an oceanic port. To the west, beyond Puget Sound, are the Kitsap Peninsula
The Kitsap Peninsula () lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "Kitsap", encompasses all of Kits ...
and Olympic Mountains
The Olympic Mountains are a mountain range on the Olympic Peninsula of the Pacific Northwest of the United States. The mountains, part of the Pacific Coast Ranges, are not especially high – Mount Olympus is the highest at ; however, the easter ...
on the Olympic Peninsula; to the east, beyond Lake Washington and the Eastside suburbs, are Lake Sammamish
Lake Sammamish is a freshwater lake east of Seattle in King County, Washington, United States. The lake is long and wide, with a maximum depth of and a surface area of . It lies east of Lake Washington and west of the Sammamish Plateau, and ...
and the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
. Lake Washington's waters flow to Puget Sound through the Lake Washington Ship Canal
The Lake Washington Ship Canal, which runs through the city of Seattle, connects the fresh water body of Lake Washington with the salt water inland sea of Puget Sound. The Hiram M. Chittenden Locks accommodate the approximately difference in w ...
(consisting of two man-made canals, Lake Union
Lake Union is a freshwater lake located entirely within the city limits of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is a major part of the Lake Washington Ship Canal, which carries fresh water from the much larger Lake Washington on the east to ...
, and the Hiram M. Chittenden Locks
The Hiram M. Chittenden Locks, or Ballard Locks, is a complex of locks at the west end of Salmon Bay in Seattle, Washington's Lake Washington Ship Canal, between the neighborhoods of Ballard to the north and Magnolia to the south.
The Ballard L ...
at Salmon Bay
Salmon Bay is a portion of the Lake Washington Ship Canal, which passes through the city of Seattle, linking Lake Washington to Puget Sound, lying west of the Fremont Cut. It is the westernmost section of the canal and empties into Puget Sound' ...
, ending in Shilshole Bay
Shilshole Bay is the part of Puget Sound east of a line drawn northeasterly from Seattle's West Point in the southwest to its Golden Gardens Park in the northeast. On its shores lie Discovery Park, the Lawton Wood section of the Magnolia neighb ...
on Puget Sound).
The sea, rivers, forests, lakes, and fields surrounding Seattle were once rich enough to support one of the world's few sedentary hunter-gatherer societies. The surrounding area lends itself well to sailing, skiing, bicycling, camping, and hiking year-round.
The city itself is hilly, though not uniformly so. Like Rome, the city is said to lie on seven hills; the lists vary but typically include Capitol Hill, First Hill, West Seattle, Beacon Hill, Queen Anne, Magnolia, and the former Denny Hill. The Wallingford, Delridge, Mount Baker, Seward Park, Washington Park, Broadmoor, Madrona, Phinney Ridge, Sunset Hill, Blue Ridge, Broadview, Laurelhurst, Hawthorne Hills, Maple Leaf, and Crown Hill neighborhoods are all located on hills as well. Many of the hilliest areas are near the city center, with Capitol Hill, First Hill, and Beacon Hill collectively constituting something of a ridge along an isthmus between Elliott Bay and Lake Washington. The break in the ridge between First Hill and Beacon Hill is man-made, the result of two of the many regrading projects that reshaped the topography of the city center. The topography of the city center was also changed by the construction of a seawall and the artificial Harbor Island (completed 1909) at the mouth of the city's industrial Duwamish Waterway
Lumen Field hosted the
 Seattle's mild, temperate, marine climate allows year-round outdoor recreation, including walking, cycling, hiking, skiing, snowboarding, kayaking, rock climbing, motor boating, sailing, team sports, and swimming. In town, many people walk around Green Lake, through the forests and along the bluffs and beaches of Discovery Park (the largest park in the city) in
Seattle's mild, temperate, marine climate allows year-round outdoor recreation, including walking, cycling, hiking, skiing, snowboarding, kayaking, rock climbing, motor boating, sailing, team sports, and swimming. In town, many people walk around Green Lake, through the forests and along the bluffs and beaches of Discovery Park (the largest park in the city) in
 Seattle is a
Seattle is a
 Of the city's population over the age of 25, 53.8% (vs. a national average of 27.4%) hold a
Of the city's population over the age of 25, 53.8% (vs. a national average of 27.4%) hold a
 The University of Washington is consistently ranked among the country's leading institutions in medical research, earning special merits for programs in neurology and neurosurgery. Seattle has seen local developments of modern paramedic services with the establishment of
The University of Washington is consistently ranked among the country's leading institutions in medical research, earning special merits for programs in neurology and neurosurgery. Seattle has seen local developments of modern paramedic services with the establishment of


 The first streetcars appeared in 1889 and were instrumental in the creation of a relatively well-defined downtown and strong neighborhoods at the end of their lines. The advent of the automobile began the dismantling of rail in Seattle. Tacoma–Seattle railway service ended in 1929 and the Everett–Seattle service came to an end in 1939, replaced by automobiles running on the recently developed highway system. Rails on city streets were paved over or removed, and the opening of the Trolleybuses in Seattle, Seattle trolleybus system brought the end of Seattle Street Railway, streetcars in Seattle in 1941. This left an extensive network of privately owned buses (later public) as the only mass transit within the city and throughout the region.
King County Metro provides frequent stop bus service within the city and surrounding county, as well as the South Lake Union Streetcar line and the First Hill Streetcar line. Seattle is one of the few cities in North America whose bus fleet includes electric trolleybuses. Sound Transit provides an express bus service within the metropolitan area, two Sounder commuter rail lines between the suburbs and downtown, and its 1 Line (Sound Transit), 1 Line light rail line between the University of Washington and Angle Lake. Washington State Ferries, which manages the largest network of ferries in the United States and third largest in the world, connects Seattle to Bainbridge Island, Washington, Bainbridge and Vashon, Washington, Vashon Islands in Puget Sound and to Bremerton and Southworth, Washington, Southworth on the Kitsap Peninsula. King Street Station in Pioneer Square serves Amtrak intercity trains and Sounder commuter trains, and is located adjacent to the International District/Chinatown station, International District/Chinatown light rail station.
According to the 2007 American Community Survey, 18.6% of Seattle residents used one of the three public transit systems that serve the city, giving it the highest transit ridership of all major cities without heavy or light rail prior to the completion of Sound Transit's 1 Line. The city has also been described by Bert Sperling as the fourth most walkable U.S. city and by Walk Score as the sixth most walkable of the fifty largest U.S. cities.
The first streetcars appeared in 1889 and were instrumental in the creation of a relatively well-defined downtown and strong neighborhoods at the end of their lines. The advent of the automobile began the dismantling of rail in Seattle. Tacoma–Seattle railway service ended in 1929 and the Everett–Seattle service came to an end in 1939, replaced by automobiles running on the recently developed highway system. Rails on city streets were paved over or removed, and the opening of the Trolleybuses in Seattle, Seattle trolleybus system brought the end of Seattle Street Railway, streetcars in Seattle in 1941. This left an extensive network of privately owned buses (later public) as the only mass transit within the city and throughout the region.
King County Metro provides frequent stop bus service within the city and surrounding county, as well as the South Lake Union Streetcar line and the First Hill Streetcar line. Seattle is one of the few cities in North America whose bus fleet includes electric trolleybuses. Sound Transit provides an express bus service within the metropolitan area, two Sounder commuter rail lines between the suburbs and downtown, and its 1 Line (Sound Transit), 1 Line light rail line between the University of Washington and Angle Lake. Washington State Ferries, which manages the largest network of ferries in the United States and third largest in the world, connects Seattle to Bainbridge Island, Washington, Bainbridge and Vashon, Washington, Vashon Islands in Puget Sound and to Bremerton and Southworth, Washington, Southworth on the Kitsap Peninsula. King Street Station in Pioneer Square serves Amtrak intercity trains and Sounder commuter trains, and is located adjacent to the International District/Chinatown station, International District/Chinatown light rail station.
According to the 2007 American Community Survey, 18.6% of Seattle residents used one of the three public transit systems that serve the city, giving it the highest transit ridership of all major cities without heavy or light rail prior to the completion of Sound Transit's 1 Line. The city has also been described by Bert Sperling as the fourth most walkable U.S. city and by Walk Score as the sixth most walkable of the fifty largest U.S. cities.
Historylink.org
history of Seattle and Washington
* [http://cdm15015.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/landingpage/collection/p15015coll4 Seattle Historic Photograph Collection from the Seattle Public Library]
Seattle Civil Rights and Labor History Project
Seattle, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
{{Authority control Seattle, Cities in Washington (state) Cities in King County, Washington 1853 establishments in Oregon Territory Cities in the Seattle metropolitan area County seats in Washington (state) Isthmuses of the United States Populated places established in 1853 Populated places on Puget Sound Port settlements in Washington (state)
2009 MLS Cup
MLS Cup 2009 was the 14th edition of the MLS Cup, the championship match of Major League Soccer (MLS). The soccer match took place on November 22, 2009, at Qwest Field in Seattle, Washington, and was contested between the Los Angeles Galaxy a ...
, played between Real Salt Lake
Real Salt Lake, often shortened to RSL, is an American professional soccer franchise based in the Salt Lake City metropolitan area. The club competes as a member club of Major League Soccer (MLS) in the Western Conference. RSL began play in 20 ...
and the Los Angeles Galaxy
LA Galaxy, also known as the Los Angeles Galaxy, are an American professional soccer club based in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Galaxy competes in Major League Soccer (MLS), as a member of the Western Conference. The club began play ...
in front of 46,011 spectators. The Sounders would play their first MLS Cup at Lumen Field in 2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
, once again against Toronto FC, and won the game 3–1, earning their second MLS Cup title in front of a club-record attendance of 69,274. The stadium also hosted the second leg of the 2022 CONCACAF Champions League Final, played in front of 68,741 to break the tournament record; the Sounders became the first MLS team to win a continental title since 2000 and the first to win the modern Champions League. Seattle will be one of eleven US host cities for the 2026 FIFA World Cup with matches played at Lumen Field and training facilities at Longacres in Tukwila.
Seattle's Major League Rugby team, the Seattle Seawolves, play at Starfire Sports Complex
Starfire Sports is a multi-purpose stadium and sporting facility in Tukwila, Washington, United States. It is located on the banks of the Green River, just south of Seattle. The stadium is operated by the nonprofit corporation Starfire Sports an ...
in nearby Tukwila, a small stadium that is also used by the Sounders for their U.S. Open Cup matches. The team began play in 2018 and won the league's inaugural championship. They successfully defended the title in the 2019 season.
Seattle's professional sports history began at the start of the 20th century with the PCHA's Seattle Metropolitans
The Seattle Metropolitans were a professional ice hockey team based in Seattle, Washington, which played in the Pacific Coast Hockey Association (PCHA) from 1915 to 1924. During their nine seasons, the Metropolitans were the PCHA's most successfu ...
, which in 1917 became the first American hockey team to win the Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup (french: La Coupe Stanley) is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, an ...
.
Seattle was awarded a Major League Baseball franchise, the Seattle Pilots
The Seattle Pilots were an American professional baseball, professional baseball team based in Seattle, Washington (state), Washington during the 1969 Major League Baseball season. During their single-season existence, the Pilots played their ho ...
, in 1969. The team played at Sick's Stadium in Mount Baker
Mount Baker (Lummi: '; nok, Kw’eq Smaenit or '), also known as Koma Kulshan or simply Kulshan, is a active glacier-covered andesitic stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington in the United States. Mount ...
for one season before relocating to Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee is ...
and becoming the Milwaukee Brewers
The Milwaukee Brewers are an American professional baseball team based in Milwaukee. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) National League Central, Central division. The Brewers are named for t ...
. The city, alongside the county and state governments, sued the league and was offered a second expansion team, the Seattle Mariners
The Seattle Mariners are an American professional baseball team based in Seattle. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) American League West, West division. The team joined the American League ...
, as settlement.
The Mariners began play in 1977 at the Kingdome, where the team struggled for most of its time. Finding success in the mid-to-late 1990s saved the team from being relocated and allowed them to move to a purpose-built baseball stadium, T-Mobile Park
T-Mobile Park is a retractable roof stadium in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the home ballpark of Major League Baseball's Seattle Mariners and has a seating capacity of 47,929. It is in Seattle's SoDo neighborhood, near the western t ...
(formerly Safeco Field
T-Mobile Park is a retractable roof stadium in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the home ballpark of Major League Baseball's Seattle Mariners and has a seating capacity of 47,929. It is in Seattle's SoDo neighborhood, near the western t ...
), in 1999. The Mariners have never reached a World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the World ...
and only appeared in the MLB playoffs five times, mostly between 1995 and 2001, but had Hall of Fame players and candidates like Ken Griffey Jr., Randy Johnson
Randall David Johnson (born September 10, 1963), nicknamed "The Big Unit", is an American photographer and former professional baseball pitcher who played 22 seasons in Major League Baseball (1988–2009) for six teams, primarily the Seattle M ...
, Ichiro Suzuki
, also known mononymously as , is a Japanese former professional baseball outfielder who played professionally for 28 seasons. He played nine years of his career with the Orix BlueWave of Nippon Professional Baseball (NPB), where he began his ...
, and Alex Rodriguez
Alexander Emmanuel Rodriguez (born July 27, 1975), nicknamed "A-Rod", is an American former professional baseball shortstop and third baseman, businessman and philanthropist. Rodriguez played 22 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the ...
. The team tied the all-time MLB single regular season wins record in 2001 with 116 wins. From 2001 to 2022, the Mariners failed to qualify for the playoffs—the longest active postseason drought in major North American sports, at 20 seasons.
From 1967 to 2008, Seattle was home to the Seattle SuperSonics
The Seattle SuperSonics (commonly known as the Seattle Sonics) were an American professional basketball team based in Seattle. The SuperSonics competed in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member club of the league's Western Confe ...
of the National Basketball Association
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in North America. The league is composed of 30 teams (29 in the United States and 1 in Canada) and is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United S ...
(NBA). A frequent playoff participant, the Sonics were the 1978–79 NBA champions, and also contended for the championship in 1978
Events January
* January 1 – Air India Flight 855, a Boeing 747 passenger jet, crashes off the coast of Bombay, killing 213.
* January 5 – Bülent Ecevit, of Republican People's Party, CHP, forms the new government of Turkey (42nd go ...
and 1996
File:1996 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: A Centennial Olympic Park bombing, bomb explodes at Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, set off by a radical Anti-abortion violence, anti-abortionist; The center fuel tank explodes on TWA Flight 8 ...
. Following a team sale in 2006, a failed effort to replace the aging KeyArena
Climate Pledge Arena is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is located north of Downtown Seattle in the entertainment complex known as Seattle Center, the site of the 1962 World's Fair, for which it was ori ...
, and settlement of a lawsuit to hold the team to the final two years of its lease with the city, the SuperSonics relocated to Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, it ranks 20th among United States cities in population, a ...
and became the Oklahoma City Thunder
The Oklahoma City Thunder are an American professional basketball team based in Oklahoma City. The Thunder compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the league's Western Conference Northwest Division. The team plays i ...
ahead of the 2008–09 season. An effort in 2013 to purchase the Sacramento Kings
The Sacramento Kings are an American professional basketball team based in Sacramento, California. The Kings compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Western Conference Pacific Division. The Kings are the oldest ...
franchise and relocate it to Seattle as a resurrected Sonics squad was denied by the NBA board of governors.
The Seattle Thunderbirds
The Seattle Thunderbirds are a major junior ice hockey team based in the city of Kent, Washington, south of Seattle. They are part of the U.S. Division of the Western Conference in the Western Hockey League. They play their games at home in ac ...
hockey team plays in the Canadian major-junior Western Hockey League
The Western Hockey League (WHL) is a major junior ice hockey league based in Western Canada and the Northwestern United States. The WHL is one of three leagues that constitutes the Canadian Hockey League (CHL) as the highest level of junior h ...
and are based in the Seattle suburb of Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. Seattle successfully applied for a new expansion team with the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
called the Seattle Kraken
The Seattle Kraken are a professional ice hockey team based in Seattle. The Kraken compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Pacific Division in the Western Conference and began play during the league's 2021–22 season. ...
, who began play in 2021. A major renovation of the SuperSonics' former home arena, KeyArena (now Climate Pledge Arena
Climate Pledge Arena is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is located north of Downtown Seattle in the entertainment complex known as Seattle Center, the site of the 1962 World's Fair, for which it was or ...
) began in 2018 to accommodate the NHL team. The NHL ownership group reached its goal of 10,000 deposits within 12 minutes of opening a ticket drive, which later increased to 25,000 in 75 minutes.
The city hosted the Seattle Reign FC
OL Reign is an American professional women's soccer team based in Seattle, Washington. Founded by Bill and Teresa Predmore in 2012 as Seattle Reign FC, it was one of eight inaugural members of the National Women's Soccer League (NWSL). In 2020, ...
, a founding member of the National Women's Soccer League
The National Women's Soccer League (NWSL) is a professional women's soccer league at the top of the United States league system. It is owned by the teams and, until 2020, was under a management contract with the United States Soccer Federatio ...
, from 2014 to 2018. Formed in 2012, it was named in honor of the Seattle Reign
OL Reign is an American professional women's soccer team based in Seattle, Washington. Founded by Bill and Teresa Predmore in 2012 as Seattle Reign FC, it was one of eight inaugural members of the National Women's Soccer League (NWSL). In 2020, ...
, a women's professional basketball team that played from 1996 to 1998 in the American Basketball League, a precursor to the WNBA. The club played at Starfire Sports Complex in Tukwila for the league's inaugural 2013 season before moving to Seattle Center
Seattle Center is an arts, educational, tourism and entertainment center in Seattle, Washington, United States. Spanning an area of 74 acres (30 ha), it was originally built for the 1962 World's Fair. Its landmark feature is the tall Space Needl ...
's Memorial Stadium in 2014. Under new management, the team moved to Tacoma's Cheney Stadium
Cheney Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium located in Tacoma, Washington, United States. Originally built for baseball, the stadium is currently home to the Tacoma Rainiers of the Pacific Coast League, as well as professional soccer club Tacoma Def ...
in 2019, playing as the Reign FC. In 2020, OL Groupe, the parent company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
of French clubs Olympique Lyonnais
Olympique Lyonnais (), commonly referred to as simply Lyon () or OL, is a men and women's French professional football club based in Lyon in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. The men play in France's highest football division, Ligue 1. Founded in 1950, th ...
and Olympique Lyonnais Féminin
Olympique Lyonnais Féminin (; commonly referred to as Olympique Lyon, Lyon, or simply OL) is a French women's football club based in Lyon. The club has been the female section of Olympique Lyonnais since 2004. It is the most successful club ...
, became the team's majority owner and rebranded the club as OL Reign. The team moved back to Seattle in 2022 and currently plays in Lumen Field.
Seattle also fielded the Seattle Sea Dragons
The Seattle Sea Dragons (formerly known as the Seattle Dragons) are a professional American football team based in Seattle, Washington. The team is a franchise of the new XFL and plays its home games at Lumen Field in Seattle. Originally founde ...
of the XFL
XFL may refer to:
Sports
* XFL (2001), a defunct American football league that played its only season in 2001
* XFL (2020), a professional American football league
Vehicles
* Bell XFL Airabonita, a 1940 U.S. Navy experimental interceptor aircra ...
, who played at Lumen Field in 2020. The league suspended operations five weeks into its inaugural season due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
, eventually filed for bankruptcy, and had its assets sold. The Sea Dragons will return in the 2023 XFL season
The 2023 XFL season is the league's second season, the first planned under its new ownership group of Dwayne Johnson, Dany Garcia, and Gerry Cardinale (RedBird Capital), and the third in the history of the XFL brand created and originally owned by ...
.
The Major League Baseball All-Star Game
The Major League Baseball All-Star Game, also known as the "Midsummer Classic", is an annual professional baseball game sanctioned by Major League Baseball (MLB) and contested between the all-stars from the American League (AL) and National ...
was held in Seattle twice, first at the Kingdome in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
and again at Safeco Field in 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which Casualties of the September 11 attacks, killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a Participants in ...
. The NBA All-Star Game
The National Basketball Association All-Star Game is a basketball exhibition game hosted every February by the National Basketball Association (NBA) and showcases 24 of the league's star players. It is the featured event of NBA All-Star Weekend, a ...
was also held in Seattle twice: the first in 1974
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; f ...
at the Seattle Center Coliseum
Climate Pledge Arena is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is located north of Downtown Seattle in the entertainment complex known as Seattle Center, the site of the 1962 World's Fair, for which it was or ...
and the second in 1987
File:1987 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The MS Herald of Free Enterprise capsizes after leaving the Port of Zeebrugge in Belgium, killing 193; Northwest Airlines Flight 255 crashes after takeoff from Detroit Metropolitan Airport, k ...
at the Kingdome.
Seattle also boasts two collegiate sports teams based at the University of Washington and Seattle University
Seattle University (SeattleU) is a private Jesuit university in Seattle, Washington. Seattle University is the largest independent university in the Northwestern United States, with over 7,500 students enrolled in undergraduate and graduate prog ...
, both competing in NCAA Division I
NCAA Division I (D-I) is the highest level of College athletics, intercollegiate athletics sanctioned by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States, which accepts players globally. D-I schools include the major ...
for various sports. The University of Washington's athletic program, nicknamed the Huskies
Husky is a general term for a dog used in the polar regions, primarily and specifically for work as sled dogs. It refers to a traditional northern type, notable for its cold-weather tolerance and overall hardiness. Modern racing huskies that mai ...
, competes in the Pac-12 Conference
The Pac-12 Conference is a collegiate List of NCAA conferences, athletic conference, that operates in the Western United States, participating in 24 sports at the NCAA Division I level. Its College football, football teams compete in the NCAA D ...
, and Seattle University's athletic program, nicknamed the Redhawks, mostly competes in the Western Athletic Conference
The Western Athletic Conference (WAC) is an NCAA Division I conference. The WAC covers a broad expanse of the western United States with member institutions located in Arizona, California, New Mexico, Utah, Washington (state), Washington, and Texa ...
. The Huskies teams use several facilities, including the 70,000-seat Husky Stadium
Husky Stadium (officially Alaska Airlines Field at Husky Stadium for sponsorship purposes) is an outdoor football stadium in the northwest United States, located on the campus of the University of Washington in Seattle, Washington. It h ...
for football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
and the Hec Edmundson Pavilion
Alaska Airlines Arena at Hec Edmundson Pavilion (formerly and still commonly referred to as Hec Edmundson Pavilion or simply Hec Ed) is an indoor arena in the northwest United States, on the campus of the University of Washington in ...
for basketball and volleyball. The two schools have basketball and soccer teams that compete against each other in non-conference games and have formed a local rivalry due to their sporting success.
Parks and recreation
 Seattle's mild, temperate, marine climate allows year-round outdoor recreation, including walking, cycling, hiking, skiing, snowboarding, kayaking, rock climbing, motor boating, sailing, team sports, and swimming. In town, many people walk around Green Lake, through the forests and along the bluffs and beaches of Discovery Park (the largest park in the city) in
Seattle's mild, temperate, marine climate allows year-round outdoor recreation, including walking, cycling, hiking, skiing, snowboarding, kayaking, rock climbing, motor boating, sailing, team sports, and swimming. In town, many people walk around Green Lake, through the forests and along the bluffs and beaches of Discovery Park (the largest park in the city) in Magnolia
''Magnolia'' is a large genus of about 210 to 340The number of species in the genus ''Magnolia'' depends on the taxonomic view that one takes up. Recent molecular and morphological research shows that former genera ''Talauma'', ''Dugandiodendro ...
, along the shores of Myrtle Edwards Park
Myrtle Edwards Park in Seattle, Washington (state), Washington is a public park along the Elliott Bay waterfront north of Belltown, Seattle, Belltown. It features a long bicycle and walking path and is a good place to see eagles, gulls, and cr ...
on the Downtown waterfront, along the shoreline of Lake Washington at Seward Park, along Alki Beach in West Seattle, or along the Burke-Gilman Trail. Gas Works Park
Gas Works Park is a park located in Seattle, Washington, United States. It is a public park on the site of the former Seattle Gas Light Company gasification plant, located on the north shore of Lake Union at the south end of the Wallingford ne ...
features the preserved superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
of a coal gasification Coal gasification is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapour (H2O)—from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
Historically, coal ...
plant closed in 1956. Located across Lake Union from downtown, the park provides panoramic views of the Seattle skyline. Also popular are hikes and skiing in the nearby Cascade or Olympic Mountains and kayaking and sailing in the waters of Puget Sound, the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
, and the Strait of Georgia
The Strait of Georgia (french: Détroit de Géorgie) or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada and the extreme northwestern mainland coast ...
. In 2005, ''Men's Fitness
''Men's Fitness'' was a men's magazine published by American Media, Inc and founded in the United States in 1987. The premier issue featured Michael Pare from the television series ''The Greatest American Hero''.
The magazine's slogan was "How th ...
'' magazine named Seattle the fittest city in the United States.
Government and politics
 Seattle is a
Seattle is a charter city
In the United States, a charter city is a city in which the governing system is defined by the city's own charter document rather than solely by general law. In states where city charters are allowed by law, a city can adopt or modify its organ ...
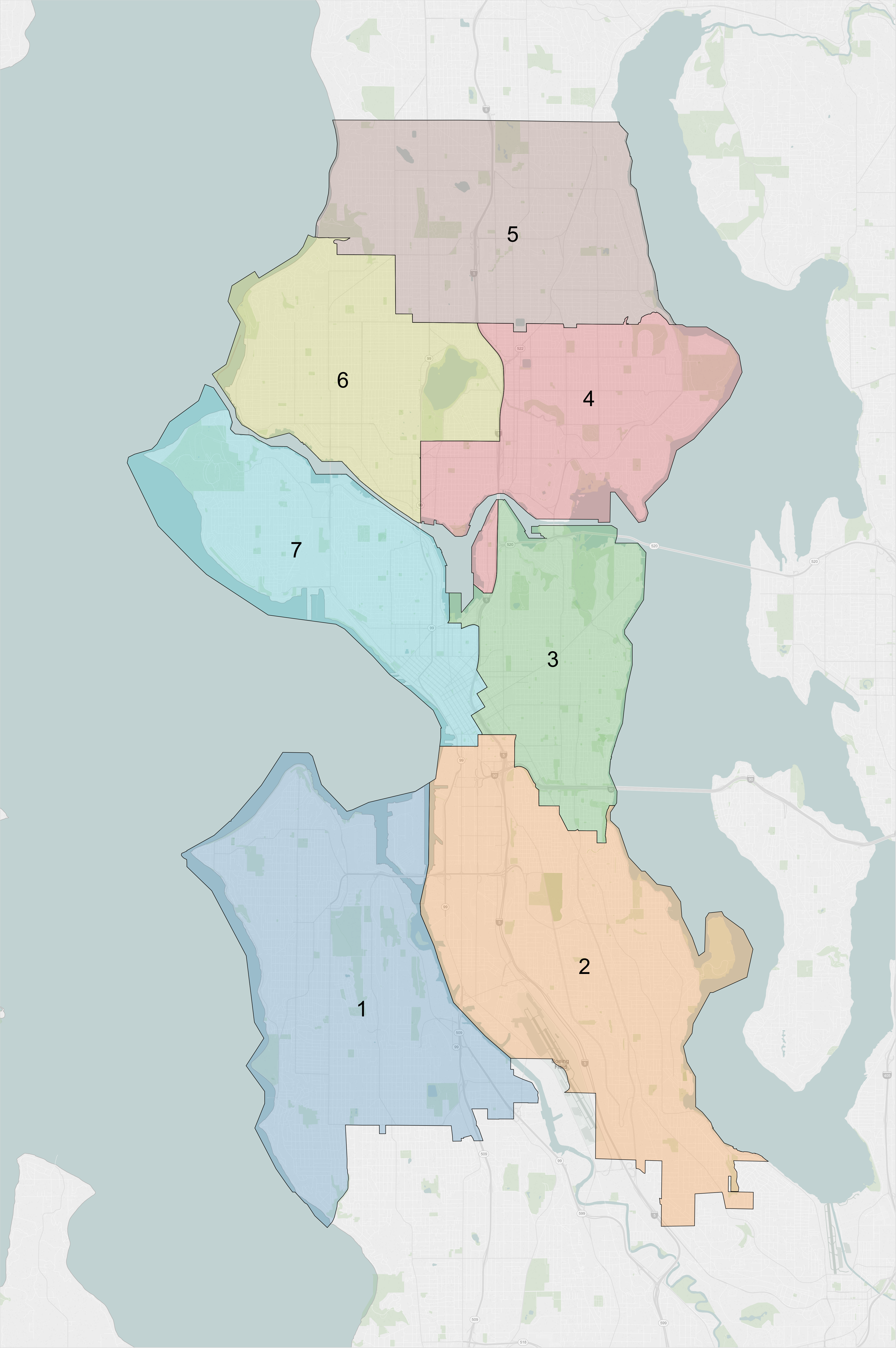
, with a mayor–council form of government. From 1911 to 2013, Seattle's nine city councillors were elected at large, rather than by geographic subdivisions. For the 2015 election, this changed to a hybrid system of seven district members and two at-large members as a result of a ballot measure passed on November 5, 2013. The only other elected offices are the city attorney
A city attorney is a position in city and municipal government in the United States. The city attorney is the attorney representing the municipality.
Unlike a district attorney or public defender, who usually handles criminal cases, a city at ...
and Municipal Court judges. All city offices are officially non-partisan
Nonpartisanism is a lack of affiliation with, and a lack of bias towards, a political party.
While an Oxford English Dictionary definition of ''partisan'' includes adherents of a party, cause, person, etc., in most cases, nonpartisan refers sp ...
. Like some other parts of the United States, government and laws are also run by a series of ballot initiatives (allowing citizens to pass or reject laws), referendums (allowing citizens to approve or reject legislation already passed), and propositions (allowing specific government agencies to propose new laws or tax increases directly to the people).
Seattle is widely considered one of the most socially liberal cities in the United States, even surpassing Portland. In the 2012 U.S. general election, a majority of Seattleites voted to approve Referendum 74 and legalize gay marriage in Washington state. In the same election, an overwhelming majority of Seattleites also voted to approve the legalization of the recreational use of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
in the state. Like much of the Pacific Northwest (which has the lowest rate of church attendance
Church attendance is a central religious practice for many Christians; some Christian denominations, such as the Catholic Church require church attendance on the Lord's Day (Sunday); the Westminster Confession of Faith is held by the Reformed Ch ...
in the United States and consistently reports the highest percentage of atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
), church attendance, religious belief, and political influence of religious leaders are much lower than in other parts of America. Seattle's political culture is very liberal and progressive for the United States, with over 80% of the population voting for the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
. All precincts in Seattle voted for Democratic Party candidate Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
in the 2012 presidential election. In partisan elections for the Washington State Legislature
The Washington State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a bicameral body, composed of the lower Washington House of Representatives, composed of 98 Representatives, and the upper Washington State Senat ...
and United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
, nearly all elections are won by Democrats. Although local elections are nonpartisan, most of the city's elected officials are known to be Democrats.
In 1926, Seattle became the first major American city to elect a female mayor, Bertha Knight Landes. It has also elected an openly gay mayor, Ed Murray, and a third-party socialist councillor, Kshama Sawant
Kshama Sawant (; born October 17, 1973) is an Indian-American politician and economist who has served on the Seattle City Council since 2014. She is a member of Socialist Alternative (United States), Socialist Alternative, the first and only mem ...
. For the first time in United States history, an openly gay black woman was elected to public office when Sherry Harris
Sherry ( es, jerez ) is a fortified wine made from white grapes that are grown near the city of Jerez de la Frontera in Andalusia, Spain. Sherry is produced in a variety of styles made primarily from the Palomino grape, ranging from light versi ...
was elected as a Seattle city councillor in 1991. In 2015, the majority of the city council was female.
Federally, Seattle is split between two congressional districts. Most of the city is in Washington's 7th congressional district
Washington's 7th congressional district encompasses most of Seattle and Burien, and all of Vashon Island, Lake Forest Park, Edmonds, Shoreline, and Normandy Park. Since 2017, the 7th district has been represented in the U.S. House of Represe ...
, represented by Democrat Pramila Jayapal
Pramila Jayapal ( ; born September 21, 1965) is an American politician serving as the United States House of Representatives, U.S. representative from since 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, she represents ...
, the first Indian-American woman elected to Congress. She succeeded 28-year incumbent and fellow Democrat Jim McDermott
James Adelbert McDermott (born December 28, 1936) is an American politician and psychiatrist who was the U.S. representative for from 1989 to 2017. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The 7th District includes most of Seattle, Vashon Isla ...
. Part of southeastern Seattle is in the 9th District, represented by Democrat Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
.
Bruce Harrell
Bruce Allen Harrell (born October 10, 1958) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 57th and current mayor of Seattle, Washington. He served as a member of the Seattle City Council from District 2 from 2016 to 2020. Elected to the c ...
was elected as mayor in the 2021 mayoral election, succeeding Jenny Durkan
Jenny Anne Durkan (born May 19, 1958) is an American attorney, former federal prosecutor, and politician who served as the 56th mayor of Seattle, Washington. She is the daughter of Martin Durkan. Durkan is a member of the Democratic Party. Afte ...
, and took office on January 1, 2022. The mayor's office also includes three deputy mayor
The deputy mayor (also known as vice mayor, assistant mayor, or mayor ''pro tem'') is an elective or appointive office of the second-ranking official that is present in many, but not all, local governments.
Duties and functions
Many elected dep ...
s, appointed to advise the mayor on policies. As of 2022, the city's deputy mayors are Monisha Harrell, Tiffany Washington, and Kendee Yamaguchi.
Education
 Of the city's population over the age of 25, 53.8% (vs. a national average of 27.4%) hold a
Of the city's population over the age of 25, 53.8% (vs. a national average of 27.4%) hold a bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six ...
or higher, and 91.9% (vs. 84.5% nationally) have a high school diploma or equivalent
Equivalence or Equivalent may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Album-equivalent unit, a measurement unit in the music industry
* Equivalence class (music)
*'' Equivalent VIII'', or ''The Bricks'', a minimalist sculpture by Carl Andre
*''Equiva ...
. A 2008 United States Census Bureau survey showed that Seattle had the highest percentage of college and university graduates of any major U.S. city. The city was listed as the most literate of the country's 69 largest cities in 2005 and 2006, the second most literate in 2007 and the most literate in 2008 in studies conducted by Central Connecticut State University
Central Connecticut State University (Central Connecticut, CCSU, Central Connecticut State, or informally Central) is a public university in New Britain, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1849 as the State Normal School, CCSU is Connecticut ...
.
Seattle Public Schools
Seattle Public Schools is the largest Public school (government funded), public school district in the state of Washington (state), Washington. The school district serves almost all of Seattle. Additionally it includes sections of Boulevard Park, ...
is the school district for the vast majority of the city. That school district desegregated without a court order but continue to struggle to achieve racial balance in a somewhat ethnically divided city (the south part of town having more ethnic minorities than the north). In 2007, Seattle's racial tie-breaking system was struck down by the United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
, but the ruling left the door open for desegregation formulae based on other indicators (e.g., income or socioeconomic class). A very small portion of the city is within the Highline School District
Highline Public Schools (HPS) is a public school district in King County, headquartered in Burien, Washington. As of October 2007, it served 17,331 students and had 997 teachers, and served the cities of Burien, much of Des Moines, Normandy Park ...
.
The public school system is supplemented by a moderate number of private schools: Five of the private high schools are Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, one is Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
, and six are secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
.
Seattle is home to the University of Washington, as well as the institution's professional and continuing education unit, the University of Washington Educational Outreach. The 2017 ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked the University of Washington at No. 11 in the world. The UW receives more federal research and development funding than any public institution. Over the last 10 years, it has also produced more Peace Corps volunteers than any other U.S. university. Seattle also has a number of smaller private universities including Seattle University
Seattle University (SeattleU) is a private Jesuit university in Seattle, Washington. Seattle University is the largest independent university in the Northwestern United States, with over 7,500 students enrolled in undergraduate and graduate prog ...
and Seattle Pacific University
Seattle Pacific University (SPU) is a private Christian university in Seattle, Washington. It was founded in 1891 in conjunction with the Oregon and Washington Conference of the Free Methodist Church as the Seattle Seminary. It became the Seat ...
, the former a Jesuit Catholic institution, the latter a Free Methodist institution. The Seattle Colleges District
The Seattle Colleges District (previously Seattle Community Colleges District), also known simply as Seattle Colleges, is a group of colleges located in Seattle, Washington. It consists of three colleges—North Seattle College, Seattle Central ...
operates three colleges: North Seattle College
North Seattle College (NSC or North Seattle) is a public college in the northwest United States, located in Seattle, Washington. It is one of three colleges comprising the Seattle Colleges District and part of the Washington Community and ...
, Seattle Central College
Seattle Central College is a public college in Seattle, Washington. With North Seattle College and South Seattle College, it is one of the three colleges that comprise the Seattle Colleges District. The college has a substantial internatio ...
, and South Seattle College
South Seattle College (SSC, formerly South Seattle Community College) is a public community college in West Seattle, Washington. Founded in 1970, it is one of three colleges which make up the Seattle Colleges District. The Seattle Community Colle ...
. Universities aimed at the working adult are the City University and Antioch University
Antioch University is a private university with multiple campuses in the United States and online programs. Founded in 1852 as Antioch College, its first president was politician, abolitionist, and education reformer Horace Mann. It changed its n ...
. Seminaries include Western Seminary
Western Seminary is an interdenominational Evangelical Christian seminary with campuses in Portland, Oregon; San Jose, California; and Sacramento, California. Western Seminary also has online-only degrees and programs and provides non-credit cla ...
and a number of arts colleges, such as Cornish College of the Arts
Cornish College of the Arts (CCA) is a private art college in Seattle, Washington. It was founded in 1914.
History
Cornish College of the Arts was founded in 1914 as the Cornish School of Music, by Nellie Cornish (1876–1956), a teacher of pi ...
, Pratt Fine Arts Center
Pratt Fine Arts Center is a non-profit arts education and resource center in the Squire Park area of Seattle's Central District. The center employs 155 teaching artists and conducts more than 600 classes annually.
Pratt was founded in 1976 by ...
. In 2001, ''Time'' magazine selected Seattle Central Community College as community college of the year, saying that the school "pushes diverse students to work together in small teams".
Media
, Seattle has one major daily newspaper, ''The Seattle Times
''The Seattle Times'' is a daily newspaper serving Seattle, Washington, United States. It was founded in 1891 and has been owned by the Blethen family since 1896. ''The Seattle Times'' has the largest circulation of any newspaper in Washington (s ...
''. The ''Seattle Post-Intelligencer
The ''Seattle Post-Intelligencer'' (popularly known as the ''Seattle P-I'', the ''Post-Intelligencer'', or simply the ''P-I'') is an online newspaper and former print newspaper based in Seattle, Washington, United States.
The newspaper was foun ...
'', known as the ''P-I'', published a daily newspaper from 1863 to March 17, 2009, before switching to a strictly on-line publication. There is also the ''Seattle Daily Journal of Commerce
The ''Seattle Daily Journal of Commerce'' is a daily (six days per week) newspaper based in Seattle, Washington. Specializing in business, construction, real estate, and legal news and public notices, it began publication in 1895 as the ''Bullet ...
'', and the University of Washington publishes '' The Daily'', a student-run publication, when school is in session. The most prominent weeklies are the ''Seattle Weekly
The ''Seattle Weekly'' is an alternative biweekly distributed newspaper in Seattle, Washington, United States. It was founded by Darrell Oldham and David Brewster as ''The Weekly.'' Its first issue was published on March 31, 1976. The newspaper ...
'' and '' The Stranger''; both consider themselves "alternative" papers. The weekly LGBT newspaper is the ''Seattle Gay News
The ''Seattle Gay News'' is a weekly newspaper aimed at the Seattle and Puget Sound area LGBT community in the U.S. state of Washington.
History
''Seattle Gay News'' was founded in 1974 by Jim Tully and Jim Anderson. As of 2022, the SGN is dist ...
''. ''Real Change
''Real Change'' is a weekly progressive street newspaper based in Seattle, Washington, USA written by professional staff and sold by self-employed vendors, many of whom are homeless. The paper provides them with an alternative to panhandling ...
'' is a weekly street newspaper that is sold mainly by homeless
Homelessness or houselessness – also known as a state of being unhoused or unsheltered – is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and adequate housing. People can be categorized as homeless if they are:
* living on the streets, also kn ...
persons as an alternative to panhandling. There are also several ethnic newspapers, including '' The Facts'', ''Northwest Asian Weekly
The ''Northwest Asian Weekly'' is a weekly Asian American newspaper based in Seattle, Washington's International District. Distributed for free, it was founded in 1982 by Assunta Ng, founder of the '' Seattle Chinese Post''. It has a circulation ...
'' and the ''International Examiner
The ''International Examiner'' is a free biweekly Asian American newspaper based in Seattle, Washington's International District. It was founded in 1974 by Gerald Yuasa and Lawrence Imamura to serve what the founders thought were the business int ...
'' as well as numerous neighborhood newspapers.
Seattle is also well served by television and radio, with all major U.S. networks represented, along with at least five other English-language stations and two Spanish-language stations. Seattle cable viewers also receive CBUT
CBUT-DT (channel 2) is a television station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, serving as the West Coast flagship of CBC Television. It is part of a twinstick with Ici Radio-Canada Télé station CBUFT-DT (channel 26). Both stations sh ...
2 ( CBC) from Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, British Columbia.
Non-commercial
A non-commercial (also spelled noncommercial) activity is an activity that does not, in some sense, involve commerce, at least relative to similar activities that do have a commercial objective or emphasis. For example, advertising-free community ...
radio stations include NPR
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other ...
affiliates KUOW-FM
KUOW-FM (94.9 MHz) is a National Public Radio member station in Seattle, Washington. It is the largest of the three full-fledged NPR member stations in the Seattle and Tacoma media market, with two Tacoma-based stations, KNKX and KVTI being the ...
94.9 and KNKX
KNKX (88.5 MHz) is a public radio station licensed to Tacoma, Washington, United States. A member of National Public Radio (NPR), it airs a jazz and news format for the Seattle metropolitan area. The station is owned by Pacific Public Medi ...
88.5 (Tacoma), as well as classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" also ...
station KING-FM
KING-FM (98.1 MHz; "Classical King FM") is a non-commercial classical music radio station in Seattle, Washington. It is owned by Classic Radio, a nonprofit organization. The studios and offices are on Mercer St in Seattle. KING-FM holds period ...
98.1. Other non-commercial stations include KEXP-FM
KEXP-FM (90.3 MHz) is a non-commercial radio station licensed to Seattle, Washington, United States, specializing in alternative and indie rock programmed by its disc jockeys for the Seattle metropolitan area. The station is owned by the non-pr ...
90.3 (affiliated with the UW), community radio
Community radio is a radio service offering a third model of radio broadcasting in addition to commercial and public broadcasting. Community stations serve geographic communities and communities of interest. They broadcast content that is popular ...
KBCS-FM 91.3 (affiliated with Bellevue College
Bellevue College (BC) is a public college in Bellevue, Washington, United States. It is the largest of the 34 institutions that make up the Washington Community and Technical Colleges system and the third-largest institution of higher educati ...
), and high school radio
High school radio are radio stations located at high schools and usually operated by its students with faculty supervision. The oldest extant high school AM radio station is AM 1450 KBPS in Portland, Oregon. Portland radio station KBPS, first li ...
KNHC-FM
KNHC (89.5 FM broadcasting, FM) is a List of broadcast station classes#FM, Class C1 high school radio station based in Seattle, Seattle, Washington. It is the world's oldest, still remaining, dance music station.
C89.5 offers a hybrid of current ...
89.5, which broadcasts an electronic dance music radio format
A radio format or programming format (not to be confused with broadcast programming) describes the overall content broadcast on a radio station. The radio format emerged mainly in the United States in the 1950s, at a time when Radio broadcasting, ...
, is owned by the public school system and operated by students of Nathan Hale High School Nathan Hale High School may refer to:
* Nathan Hale High School (Oklahoma), United States
* Nathan Hale High School (Washington), United States
* Nathan Hale High School (Wisconsin), United States
* Nathan Hale-Ray High School, Connecticut
...
. Many Seattle radio stations are available through Internet radio
Online radio (also web radio, net radio, streaming radio, e-radio, IP radio, Internet radio) is a digital audio service transmitted via the Internet. Broadcasting on the Internet is usually referred to as webcasting since it is not transmitted ...
, with KEXP in particular being a pioneer of Internet radio. Seattle also has numerous commercial radio stations. In a March 2012 report by the consumer research firm Arbitron
Nielsen Audio (formerly Arbitron) is a consumer research company in the United States that collects listener data on radio broadcasting audiences. It was founded as the American Research Bureau by Jim Seiler in 1949 and became national by mergin ...
, the top FM stations were KRWM
KRWM (106.9 FM) is a commercial radio station licensed to Bremerton, Washington, serving the Seattle/ Puget Sound region. It is owned by Hubbard Broadcasting, and airs an adult contemporary radio format. The station switches to all-Christmas m ...
(adult contemporary
Adult contemporary music (AC) is a form of radio-played popular music, ranging from 1960s vocal and 1970s soft rock music to predominantly ballad-heavy music of the present day, with varying degrees of easy listening, pop, soul, R&B, quie ...
format), KIRO-FM
KIRO-FM (97.3 MHz) is a commercial radio station licensed to Tacoma, Washington, and serving the Seattle-Tacoma radio market. It airs a news/talk radio format and is owned by Salt Lake City–based Bonneville International, a broadcasting compa ...
(news/talk
Talk radio is a radio format containing discussion about topical issues and consisting entirely or almost entirely of original spoken word content rather than outside music. Most shows are regularly hosted by a single individual, and often featur ...
), and KISW
KISW (99.9 FM) – branded 99.9 KISW, The Rock of Seattle – is a commercial mainstream rock radio station licensed to Seattle, Washington. Owned by Audacy, Inc., the station serves the Seattle metropolitan area; live shows include ''The Me ...
(active rock
Active rock is a radio format used by many commercial radio stations across the United States and Canada. Active rock stations play a balance of new hard rock songs with valued classic rock favorites, normally with an emphasis on the harder edge o ...
) while the top AM stations were KOMO (all news
All-news radio is a radio format devoted entirely to the discussion and broadcast of news.
All-news radio is available in both local and syndicated forms, and is carried on both major US satellite radio networks. All-news stations can run the ...
), KJR (AM)
KJR (950 kHz) is an all-sports AM radio station owned by iHeartMedia in Seattle, Washington. KJR is the Puget Sound region's home of Fox Sports Radio and CBS Sports Radio, mostly carrying their national programming, while co-owned 93.3 KJR-FM ...
(all sports
All Sports is the first greatest hits album by Australian rock and pop band The Sports, released in December 1982. The album peaked at number 35 on the Australian Kent Music Report.
Reception
Steve Schnee from AllMusic
AllMusic (previou ...
), KIRO (AM)
KIRO (710 kHz "Seattle Sports") is a commercial AM radio station in Seattle, Washington, owned by Salt Lake City–based Bonneville International. The station airs a sports radio format and is an ESPN Radio Network affiliate. The station's stu ...
(all sports).
Seattle-based online magazines Worldchanging
Worldchanging was a nonprofit online publisher that operated from 2003 to 2010. Its strapline was ''A bright green future''. It published newsletters and books about sustainability, bright green environmentalism, futurism and social innovation.
...
and Grist.org
''Grist'' (originally ''Grist Magazine''; also referred to as Grist.org) is an American non-profit online magazine founded in 1999 that publishes environmental news and commentary. ''Grists tagline is "Climate. Justice. Solutions." ''Grist'' ...
were two of the "Top Green Websites" in 2007 according to TIME.
Infrastructure
Health systems
 The University of Washington is consistently ranked among the country's leading institutions in medical research, earning special merits for programs in neurology and neurosurgery. Seattle has seen local developments of modern paramedic services with the establishment of
The University of Washington is consistently ranked among the country's leading institutions in medical research, earning special merits for programs in neurology and neurosurgery. Seattle has seen local developments of modern paramedic services with the establishment of Medic One
The Seattle & King County Emergency Medical Services System is a fire-based two-tier response system providing prehospital basic and advanced life support services.
There are six paramedic provider programs in the system. The Seattle Fire Departm ...
in 1970. In 1974, a ''60 Minutes
''60 Minutes'' is an American television news magazine broadcast on the CBS television network. Debuting in 1968, the program was created by Don Hewitt and Bill Leonard, who chose to set it apart from other news programs by using a unique styl ...
'' story on the success of the then four-year-old Medic One paramedic system called Seattle "the best place in the world to have a heart attack". Three of Seattle's largest medical centers are located on First Hill. Harborview Medical Center
Harborview Medical Center is a public hospital located in the First Hill neighborhood of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is managed by UW Medicine.
Overview
Harborview Medical Center is the designated Disaster Control Hospital for Seattl ...
, the public county hospital, is the only Level I trauma hospital in a region that includes Washington, Alaska, Montana, and Idaho. Virginia Mason Medical Center
Virginia Mason Medical Center is an integrated hospital, training and research facility located in Seattle, Washington, USA. It was the founding location, in 1920, of the private, non-profit Virginia Mason health organization; in January 2021, the ...
and Swedish Medical Center
Swedish Health Services, formerly Swedish Medical Center, is the largest nonprofit health provider in the Seattle metropolitan area. It operates five hospital campuses (in the Seattle neighborhoods of First Hill, Cherry Hill and Ballard, and th ...
's two largest campuses are also located in this part of Seattle, including the Virginia Mason Hospital
Virginia Mason Hospital is a 336-bed teaching hospital in Seattle, Washington, part of the Virginia Mason Medical Center. The hospital is accredited by the Joint Commission and the Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF). F ...
. This concentration of hospitals resulted in the neighborhood's nickname "Pill Hill". Located in the Laurelhurst neighborhood, Seattle Children's
Seattle Children's, formerly Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, formerly Children's Orthopedic Hospital, is a children's hospital in the Laurelhurst neighborhood of Seattle, Washington. The hospital specializes in the care of inf ...
, formerly Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center
Seattle Children's, formerly Children's Hospital and Regional Medical Center, formerly Children's Orthopedic Hospital, is a children's hospital in the Laurelhurst neighborhood of Seattle, Washington. The hospital specializes in the care of infa ...
, is the pediatric referral center for Washington, Alaska, Montana, and Idaho. The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, formerly known as the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and also known as Fred Hutch or The Hutch, is a cancer research institute established in 1975 in Seattle, Washington.
History
The center grew out o ...
has a campus in the Eastlake neighborhood. The University District is home to the University of Washington Medical Center
The University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) is a hospital in the University District of Seattle, Washington. It is one of the teaching hospitals affiliated with the University of Washington School of Medicine.And is located in the War ...
which, along with Harborview, is operated by the University of Washington. Seattle is also served by a Veterans Affairs
Veterans' affairs is an area of public policy concerned with relations between a government and its communities of military veterans. Some jurisdictions have a designated government agency or department, a Department of Veterans' Affairs, Minist ...
hospital on Beacon Hill, a third campus of Swedish in Ballard, and UW Medical Center - Northwest near Northgate Station.
Transportation



 The first streetcars appeared in 1889 and were instrumental in the creation of a relatively well-defined downtown and strong neighborhoods at the end of their lines. The advent of the automobile began the dismantling of rail in Seattle. Tacoma–Seattle railway service ended in 1929 and the Everett–Seattle service came to an end in 1939, replaced by automobiles running on the recently developed highway system. Rails on city streets were paved over or removed, and the opening of the Trolleybuses in Seattle, Seattle trolleybus system brought the end of Seattle Street Railway, streetcars in Seattle in 1941. This left an extensive network of privately owned buses (later public) as the only mass transit within the city and throughout the region.
King County Metro provides frequent stop bus service within the city and surrounding county, as well as the South Lake Union Streetcar line and the First Hill Streetcar line. Seattle is one of the few cities in North America whose bus fleet includes electric trolleybuses. Sound Transit provides an express bus service within the metropolitan area, two Sounder commuter rail lines between the suburbs and downtown, and its 1 Line (Sound Transit), 1 Line light rail line between the University of Washington and Angle Lake. Washington State Ferries, which manages the largest network of ferries in the United States and third largest in the world, connects Seattle to Bainbridge Island, Washington, Bainbridge and Vashon, Washington, Vashon Islands in Puget Sound and to Bremerton and Southworth, Washington, Southworth on the Kitsap Peninsula. King Street Station in Pioneer Square serves Amtrak intercity trains and Sounder commuter trains, and is located adjacent to the International District/Chinatown station, International District/Chinatown light rail station.
According to the 2007 American Community Survey, 18.6% of Seattle residents used one of the three public transit systems that serve the city, giving it the highest transit ridership of all major cities without heavy or light rail prior to the completion of Sound Transit's 1 Line. The city has also been described by Bert Sperling as the fourth most walkable U.S. city and by Walk Score as the sixth most walkable of the fifty largest U.S. cities.
The first streetcars appeared in 1889 and were instrumental in the creation of a relatively well-defined downtown and strong neighborhoods at the end of their lines. The advent of the automobile began the dismantling of rail in Seattle. Tacoma–Seattle railway service ended in 1929 and the Everett–Seattle service came to an end in 1939, replaced by automobiles running on the recently developed highway system. Rails on city streets were paved over or removed, and the opening of the Trolleybuses in Seattle, Seattle trolleybus system brought the end of Seattle Street Railway, streetcars in Seattle in 1941. This left an extensive network of privately owned buses (later public) as the only mass transit within the city and throughout the region.
King County Metro provides frequent stop bus service within the city and surrounding county, as well as the South Lake Union Streetcar line and the First Hill Streetcar line. Seattle is one of the few cities in North America whose bus fleet includes electric trolleybuses. Sound Transit provides an express bus service within the metropolitan area, two Sounder commuter rail lines between the suburbs and downtown, and its 1 Line (Sound Transit), 1 Line light rail line between the University of Washington and Angle Lake. Washington State Ferries, which manages the largest network of ferries in the United States and third largest in the world, connects Seattle to Bainbridge Island, Washington, Bainbridge and Vashon, Washington, Vashon Islands in Puget Sound and to Bremerton and Southworth, Washington, Southworth on the Kitsap Peninsula. King Street Station in Pioneer Square serves Amtrak intercity trains and Sounder commuter trains, and is located adjacent to the International District/Chinatown station, International District/Chinatown light rail station.
According to the 2007 American Community Survey, 18.6% of Seattle residents used one of the three public transit systems that serve the city, giving it the highest transit ridership of all major cities without heavy or light rail prior to the completion of Sound Transit's 1 Line. The city has also been described by Bert Sperling as the fourth most walkable U.S. city and by Walk Score as the sixth most walkable of the fifty largest U.S. cities.
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport , branded as SEA Airport and also referred to as Sea–Tac (), is the primary commercial airport serving the Seattle metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Washington. It is in the city of SeaTac, which ...
, locally known as Sea-Tac Airport and located just south in the neighboring city of SeaTac, is operated by the Port of Seattle and provides commercial air service to destinations throughout the world. Closer to downtown, Boeing Field is used for general aviation, cargo flights, and testing/delivery of Boeing airliners. A secondary passenger airport, Paine Field, opened in 2019 and is located in Everett, north of Seattle. It is predominantly used by Boeing and their Boeing Everett Factory, large assembly plant located nearby.
The main mode of transportation, however, is the street system, which is laid out in a cardinal directions grid plan, grid pattern, except in the central business district where early city leaders Arthur A. Denny, Arthur Denny and Carson Boren insisted on orienting the plats relative to the shoreline rather than to true North. Only two roads, Interstate 5 in Washington, Interstate 5 and Washington State Route 99, State Route 99 (both limited-access highways) run uninterrupted through the city from north to south. From 1953 to 2019, State Route 99 ran through downtown Seattle on the Alaskan Way Viaduct, an elevated freeway on the waterfront. However, due to damage sustained during the 2001 Nisqually earthquake the viaduct was replaced by a tunnel. The Alaskan Way Viaduct replacement tunnel was originally scheduled to be completed in December 2015 at a cost of US$4.25 billion. The world's largest tunnel boring machine, named "Bertha (tunnel boring machine), Bertha", was commissioned for the project, measuring in diameter. The tunnel's opening was delayed to February 2019 due to issues with the tunnel boring machine, which included a two-year halt in excavation. Seattle has the 8th worst traffic congestion of all American cities, and is 10th among all North American cities according to Inrix.
The city has started moving away from the automobile and towards mass transit. From 2004 to 2009, the annual number of unlinked public transportation trips increased by approximately 21%. In 2006, voters in King County passed the Transit Now proposition, which increased bus service hours on high ridership routes and paid for five limited-stop bus lines called RapidRide. After rejecting a Roads and Transit, roads and transit measure in 2007, Seattle-area voters passed a transit only measure in 2008 to increase ST Express bus service, extend the Link light rail system, and expand and improve Sounder commuter rail service. A light rail line (now the 1 Line (Sound Transit), 1 Line) from downtown heading south to Sea-Tac Airport began service on December 19, 2009, giving the city its first rapid transit line with intermediate stations within the city limits. An extension north to the University of Washington opened on March 19, 2016, followed by the Northgate, Seattle, Northgate extension in October 2021. Further extensions are planned to reach Lynnwood, Washington, Lynnwood to the north, Federal Way, Washington, Federal Way to the south, and Bellevue and Redmond to the east by 2025. Voters in the Puget Sound region approved an additional tax increase in November 2016 to expand light rail to West Seattle and Ballard as well as Tacoma, Everett, and Issaquah.
Utilities
Water and electric power are municipal services, provided by Seattle Public Utilities and Seattle City Light respectively. Other utility companies serving Seattle include Puget Sound Energy (natural gas, electricity), Seattle Steam Company (steam), Waste Management, Inc and Recology CleanScapes (curbside recycling, composting, and solid waste removal), CenturyLink, Frontier Communications, Wave Broadband, and Comcast (telecommunications and television). About 90% of Seattle's hydroelectricity, electricity is produced using hydropower. Less than 2% of electricity is produced using fossil fuels.International relations
Seattle has the following sister city, sister cities: * Beersheba, Israel * Bergen, Norway * Cebu City, Philippines * Chongqing, China * Christchurch, New Zealand * Daejeon, South Korea * Galway, Republic of Ireland, Ireland * Gdynia, Poland * Haiphong, Vietnam * Kaohsiung,Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
* Tashkent, Uzbekistan
* Kobe, Japan
* Limbe, Cameroon, Limbe, Cameroon
* Mombasa, Kenya
* Nantes, France
* Pécs, Hungary
* Perugia, Italy
* Reykjavík, Iceland
* Sihanoukville (city), Sihanoukville, Cambodia
* Surabaya, Indonesia
See also
* * * List of people from Seattle * List of television shows set in SeattleNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
* * * * Sanders, Jeffrey Craig. ''Seattle and the Roots of Urban Sustainability: Inventing Ecotopia'' (University of Pittsburgh Press; 2010) 288 pages; the rise of environmental activismExternal links
*Historylink.org
history of Seattle and Washington
* [http://cdm15015.contentdm.oclc.org/cdm/landingpage/collection/p15015coll4 Seattle Historic Photograph Collection from the Seattle Public Library]
Seattle Civil Rights and Labor History Project
Seattle, a National Park Service ''Discover Our Shared Heritage'' Travel Itinerary
{{Authority control Seattle, Cities in Washington (state) Cities in King County, Washington 1853 establishments in Oregon Territory Cities in the Seattle metropolitan area County seats in Washington (state) Isthmuses of the United States Populated places established in 1853 Populated places on Puget Sound Port settlements in Washington (state)